knowledge
Categories
-
1.When were rivet nut invented?+
The Rivet Nut was invented in 1936 to attach a rubber de-icer extrusion to the wing of an aircraft. It performs as a rivet to fasten two or more materials together. It performs as a nut for the attachment of a mating part with a screw.
The aerospace standards for the round body, open end, Rivet Nut, are NAS1329, (Flat Head) and NAS1330, (Countersunk Head).
In the field of aviation, rivet nuts are often used to attach various items, such as static dischargers and inspection access covers, to the surface of an aircraft.
-
2.What are the applications of rivet nuts, what are the advantages?+
Rivet nut has three main applications:
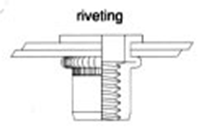
1.Riveting Application
Can be used to rivet two parts together. After the part have been riveted together, the threads on the rivet nut can be used to attach a secondary component.
2.Work from one side of the workpieces
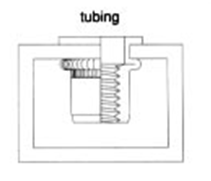
Can work from one side of the workpieces. When the situation allows, access to the backside of a workpiece makes it convenient for attaching a nut on the backside while attaching components from the front side. However, in large workpiece applications and where there is limited access to the backside, there becomes a need for an increased number of personnel or in some cases becomes impossible by traditional methods. Rivet Nuts allow you to install nuts and attach components from one side of the workpiece, saving time and labor. Rivet nuts can also be used in piping and hollow workpieces where there is limited to no access on the inner side of the application.
3.Increase thread strength capacity of thin sheets
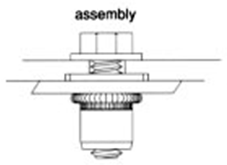
For thin metal sheet applications where thread strength is required, installation of rivet nuts can be used to supplement the number of threads and ultimately increase thread strength. Tapping of thin sheets may not meet application thread strength requirements due to limited number of threads and even inability to tap. Rivet nuts are a good alternative to supplementing thread strength capacity in thin sheet applications.
-
3.What is a rivet nut?+
A rivet nut is nut and counterbored tubular rivet merged into one component. It’s literally a nut designed for riveting application.
-
4.How many types of rivet nuts are there?+
From its invention untill now, there are thousands of types of rivet nuts in application. However, despite the vast number of spec variations, rivet nuts can be classified into the below types. Most customized parts only vary by dimension, material, and plating specs.
1. Smooth body Round Rivet Nuts: Among the world’s oldest type of rivet nuts, smooth shiny appearance with minimal special features. Despite a low spin out performance, this part offers a low cost option for rivet nut application.

2. Knurled Rivet Nuts: In order to increase the spin out performance of smooth body round rivet nuts, the knurled part series was developed. With the addition of the knurl feature on the body of the rivet nut, spin out performance increase by at least 100% of the basic design. Due to the lower tooling life and hence higher overall cost during production, knurled body parts are generally more expensive than their smooth body counterparts. Knurled rivet nuts are the most commonly used rivet nut type and account for over 50% of our company’s requested parts.
3. Semi-Hex Rivet Nuts: In applications where even higher spin out resistance is required, semi-hex parts may be used. Semi-hex parts, as the name suggests, are half hex body and half round body. The installation of the hex body into a hole creates greater resistance to spin out, an estimated 50 – 100 % increase from knurled parts. Semi-hex parts and knurled parts are similarly priced, however semi-hex parts are limited in their application in that their matching holes also need to be hex holes.

4. Full Hex Rivet Nuts: This type of rivet nut has the best spin out performance. The strength of the part is reinforced by it outer hex inner round structure, stronger and performing better than the semi-hex parts. Due to its thicker walls, the installation force of full hex parts tends to be higher, therefore also tend to require higher capacity tooling gun for installation than average thin walled parts.
5. Slotted Body Rivet Nuts: Most types of rivet nuts have a limited grip range of approximately 2 – 3mm. Slotted body rivet nuts can be used for a wider grip range. This is made possible through 4 slots along the body of the part which crimp out evenly into 4 supporting legs, wider in range than average rivet nut parts. Slotted body rivet nut parts, in thin or low strength plate applications, can achieve a very high pull out resistance; in high strength, thicker plates, however, pull out performance tends to be lower than average rivet nut parts. Due to high tooling costs of slotted body rivet nuts and complexity of the production design, this part leans towards the higher end of the pricing scale.

6. Swaging Rivet Nuts: These belong to a special class of rivet nut, with a section along the body of thickness approximately 0.2mm which collapses inwards on installation. The threaded section of the parts inserts and forms a fit with the counterbore. There is no grip range limitations with Swaging rivet nuts as their method of collapsing is not the same as regular rivet nuts, however, due to the low performance values of these parts, they are better suited for low loading force requirements. These parts are mainly used in electronic applications. Swaging rivet nuts are generally produced by CNC machining and thus incur a higher cost than cold formed rivet nuts.
7. Floating Rivet Nuts: This is Sherex Taiwan’s patented product used to resolve installation issues caused by accumulated tolerance. In large workpiece applications such as in automotive and aircrafts, there is a tendency for the final nut installed on the part to be off the required tolerance. Floating rivet nuts can provide a 1 – 3mm range of play and even a small angle of deviation, providing a solution to the tolerance issues in large piece applications. Floating Rivet nuts consist of two parts assembled together, making it a high cost part. Floating Rivet nuts are generally used in automotive and aerospace applications.
8. Short Floating Rivet Nuts: Same type as the patent floating rivet nut but with a shorter body. It is suitable for applications where panels have limited space on the back side.

9. Large Rivet Nuts: Most rivet nuts’ thread sizes are below M10, but there are many applications requiring high strength threads of M12 and above. Currently Sherex Taiwan produce round body and full hex parts up to M20. To install our large parts, we have also developed the 18,000lb Flex 18 tool gun, currently the most stable large part tool gun available on the market.
-
5.What types of material are used for rivet nuts?+
Currently, the five most common materials used for rivet nut manufacture include carbon steel, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, brass and monel, in order of popularity. Carbon steel material normally contain carbon percentages between 6 – 10%, high strength parts have carbon percentages between 20 – 25%. Aluminum alloy are used in application where reduction of weight is desired. Aluminum alloys, however, only have 60% of the strength of carbon steels, so are not suitable for applications of high bearing force. Unlike carbon steel material, stainless steels have high resistance to corrosion. Monel is used on sea vessels due to its high corrosion resistance.
-
6.What are the most common thread specs for rivet nuts?+
Rivet nut thread specs generally fall into the two classes: metric and imperial. Commonly used imperial threads are #4 to 3/4"; metric threads M3 to M20.
Most commonly used metric thread specs are:
M3、M4、M5、M6、M8、M10、M12、M16、M20
Most commonly used imperial thread specs are:
#4-40、#6-32、#8-32、#10-24、#10-32、1/4"-20、1/4"-28、5/16"-18、5/16"-24、3/8"-16、3/8"-24、1/2"-13、5/8"-11、3/4"-10 -
7.What other customized features do rivet nuts have?+
Apart from the standard rivet nut, there are a few special features as follows:
1. Closed-End Rivet Nuts: Some applications require that after installation the part is dust-proof, water-proof capable. To accomplish this function, a closed-end part has been developed which can prevent dust and water entering through the threaded section. Closed-end parts are normally longer in length and heavier than their open-end counterparts, making them costlier. Flange seals are used to reinforce water proof capabilities.
2. Seal: Some parts require added protection from dust and water intrusion. In rivet nut applications, water and dust may enter through the rear end or under the flange of the part. Closed-end parts, by their design, provide protection of water and dust from entering through their rear end. By adding a seal to the underside of the flange helps to strengthen the proof feature in the application.
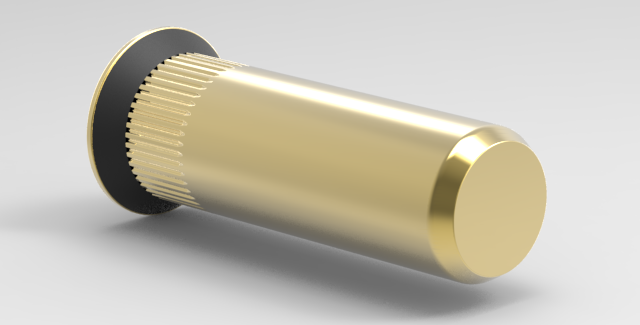
3. Wedge: Although knurled parts are the most commonly used parts for applications required spin resistance, in some instances there may be a need for an even increased spin resistance in which an application of a hex hole may not be applied. To supplement the spin out of knurled parts, wedges are added beneath the flange of the nut, which cuts into the plate material, creating an added resistance to spin in a magnitude similar to semi-hex parts. From the price perspective, wedged parts are a bit more expensive than knurled parts.
4. Square Head: In order to increase spin resistance, apart from knurl and hex features, there is another feature used to resist spinning. The flange of the part is formed into a square shape, which when placed in a hole that fits the head, created a very high spin resistance from its four sides.
-
8.How to choose the appropriate rivet nut specs.+
Firstly, the end user has to consider the environment in which the part is being used, how much load the part has to bear and how much spin resistance is required in the part. For applications in electronics bearing light loads, parts M4 and below can be used. Most applications fall within the M4 and M8 region, while high strength requirement parts are generally M10 and above. For most applications, knurled parts provide adequate resistance to spin, however, semi-hex and full hex parts are considered for higher spin resistance. Round smooth body parts are mainly used in application where low cost, low performance part is required. When plates are extremely thin or with low strength, slotted rivet nuts can be considered in the application. Floating rivet nuts are used on applications where multiple parts are installed and there are tendencies to have accumulative tolerance issues as well as hole straightness issues.
-
9.What are the installation methods for rivet nuts?+
Currently there are three main methods:
1. Torque Gun: Torque tool guns use the torque generated from the gun to provide a pulling force that installs the part. It is an efficient method that does not consider the pulling distance of the gun but simple uses an adequate torque to install the part. The most commonly used torque tool guns are air pressure spin spin guns, electric spin spin guns and other manual torque guns. Sherex’s SHT Series air pressure spin spin tool guns provide high cost-performance value options. This type of tool gun would be adequate for low volume users, however, it’s not suitable for Rivet nuts with thick walls that may require high installation force.

2. Pull Guns: This type of tool gun normally uses air and oil pressure at about 5 - 7 atmospheric pressure and converts it to over 1000kg of pulling force. This is the most ideal type of installation method as it can install all types of rivet nuts. This is the most commonly used tool in European countries. Pull guns can be used in ordinary applications and also in high strength and high installation force applications. To present there have been 4 generations of pull guns, their differences are highlighted below:
1st generation: Simple air pressure to oil pressure mechanism. Part needs to be manually installed onto the drawbar and manually removed after installation.
2nd generation: To improve the feeding of parts onto the gun, an air motor was added to the mechanism of the 1st generation tool gun. With a small force applied to the drawbar, the spindle is set off to feeding the part onto the mandrel screw. Because the torque generated by the air motor is small, the part will not be prematurely installed. After installation, the rivet nut automatically retreats from the tool gun. On average, a part is completely installed within 2 seconds, which includes feeding and retreating.
3rd generation: Third generation tool guns have been on the market for about 10 years. Sherex group’s Flex Series belongs to this unique group, its biggest difference with the 2nd generation is that the installation force can be adjusted while the 2nd generation only allows range adjustment. Due to the fact that specs of Rivet nuts can be different, even with a 0.2~0.5mm difference in length could make the part installation setting become difficult using the 2nd generation tool guns. On the contrary, the setting of the 3rd generation tool guns using installation force is very easy. Over the last 10 years, European and US markets have changed to using 3rd generation tool guns.
4th generation: As technology continues to advance, improvements continue to be made to the tool gun series. The 4th generation incorporates more electronic technology such as Bluetooth, data analysis systems, digital control of installation settings. One major feature of the 4th generation would be the monitoring screen of part installation process. The 4th generation, however, is still in the development phase and transition from the 3rd generation is still awaiting.

3. In Die: This type of installation combines stamping dies to install the parts. Most large scale factories aim to save time and resources by using large machinery to perform installation. In this case, it is not practical to install nuts by pulling on the threads. Instead the parts are installed by pressing on the rear end of the nut. This type of installation, however, is mostly suited for large scale production due to the cost of automation.
